Collagen is likely one of the most important components in our bodies. Because it is such a major part of our physiology, maintaining it plays a key role in healthy aging. This site is meant to be a resource to guide you through the vast market of amino acid collagen supplements. On this page, we will discuss the connection between collagen and aging, why dietary collagen is important, the safety of collagen supplements, how to compare supplements, and which products we recommend.
Let's start from the beginning...
Top 2 Things You Should Know About Collagen
1. Your Body's Collagen Supply is in Decline
With age, your natural ability to produce collagen slows down. The average person recieves 0% of their daily protein intake from collagen, which contributes to collagen deficiency in the body. The result is dry, thin skin, hair, and nails, as well as joint degradation and gut issues.
2. Your Body's Collagen Must Be Supported Through Diet
Just like eating fat doesn't translate to fat on your body, and eating meat doesn't directly translate into muscle, eating whole collagen will not translate immediately into better skin, joints, hair, or nails. Only enough of the right amino acids from collagen will provide your body with the building blocks it needs to repair and restore collagen.
The Collagen-Aging Connection
Did you know that our body's production of natural collagen is in sharp decline from as early as our mid twenties? This is bad news for our skin. It's even bad news for our hair, nails, gut, and joints. We believe that a collagen deficient diet leads to a collagen deficient body.
Signs of Collagen Deficiency
- Sagging skin, enlarged pores
- Fine Lines & wrinkles
- Receding gums
- Brittle Nails
- Dry Skin
- Thin, Lifeless Hair
- Joint stiffness
- Gut disorders
- Fatigue
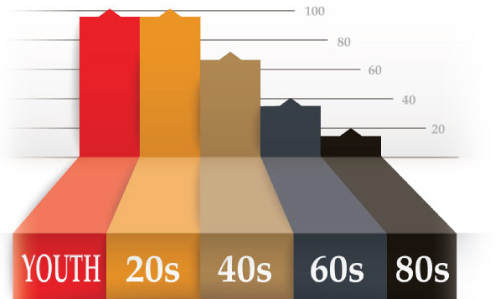
Rate of Collagen Decline From Youth
This chart is a visual of how sharply your body decreases its natural collagen production. This decline is increased even futher from sun damage. By the time we reach our 50s, collagen production is around only 50% of what it was in our youth.(6)
How to Stop Collagen Loss
While we don't know exactly what the cause of collagen decline is, it appears that individuals with a collagen-rich diet experience a slower rate of collagen loss. Recent research has connected collagen supplementation with a slower rate of collagen loss as measured on the skin. The studies showed significant improvements on the typical signs of aging in the skin, like wrinkles, skin firmness, skin suppleness and hydration. Scientists were even able to measure the effects on the collagen fibers themselves.
The fact is, individuals that consumed supplemental collagen saw significant improvements in their skin. And it was measured.
How Do Collagen Supplements Work?
Collagen supplements work by providing your body with the raw materials (amino acids) it needs to synthesize its own collagen. These amino acids are unique to collagen and cannot be found in any other protein or any other type of protein powder. A high quality hydrolyzed collagen powder will absorb fast in the body and be used right away.
Why not just eat whole collagen?
There are a couple reasons why amino collagen supplements are better than whole collagen. For one, the sources from where you would find whole collagen are in things like fish skins and cow hides, not super popular items to eat. Second, supplements are superior because they do not require digestion. Whole collagen requires digestion prior to absorption, thus, much of the benefit is lost through the digestive process.
What your body needs are the raw amino acids, the building blocks to create collagen in the body.
How Collagen is Different From Other Proteins
Collagen has a unique amino acid profile, unlike any other kind of protein. This unique balance of essential and non-essential amino acids is what makes it the beauty protein. Because some of these amino acids are difficult or impossible to find elsewhere, no wonder the average adult is collagen deficient.
The good news is, it's now so easy to put the amino acids of collagen back in the body and slow collagen loss.
What Are the Different Types of Collagen?
Collagen Safety
While collagen is generally considered safe and beneficial to the body, there can be side effects or risks associated with supplementation. And keep in mind, the FDA does not monitor supplements, so like anything you eat, do your research about before you put it in your body and make sure it's right for you.
As a side point, while most amino collagen supplements are safe, not all are equally helpful for skin and beauty. Some will help you, and some will do very litte. And some are a completely wrong type of collagen to improve the skin.
How To Choose A Collagen Supplement
- Choose marine collagen derived from fish. Why marine collagen?
- Look out for additives and hidden sugars.
You don't need added sugars or flavors with your collagen supplement. - Make sure it says "hydrolyzed" on the fact panel.
If it doesn't specify that the protein is hydrolyzed, you could be getting a gelatin, a less bioavailable form of collagen. Collagen gelatin is a good form of collagen, but if you're paying for a supplement, you might as well get the best for the same money.
Our Top Choice for Collagen Supplements
Elavonne's Amino Collagen C
- BEST SOURCE:
Collagen derived from wild caught fish and MADE IN THE USA. - BEST ABSORBENCY:
The low molecular weight of Amino Collagen C means that your body uses it more quickly and effectively. You'll see results quicker and with less calories than with other collagen supplements. - BEST FORMULA:
A high-potency formula with only marine collagen, hyaluronic acid, and vitamin C. No fillers, flavors, sugars or additives. - BEST VALUE:
Price per gram is lower than other top brands of collagen peptide.
Amino Collagen C + Hyaluronic Acid

Collagen: Eat It, Inject It, or Rub It On?
In search of the best methods for increasing collagen levels with age.
Cites and References
1. Iwal K., Hasegawa T., Taguchi Y., et al., (2006) Identification of food-derived collagen peptides in human blood after oral ingestion of gelatin hydrolysates. J Agric Food Chem 53: 6531-6535
2. Postlethwaite AE., Seyer JM., Kang AH., (1978) Chemotactic attraction of human fibroblasts to type I, II, and III collagens and collagen derived peptides. Proc Acad Sci USA 75: 871-875
3. Hitoshi Matsumoto, et al., (2006) Clinical effects of fish type I collagen hydrolysate on skin properties. ITE Letters on batteries, new technologies and medicine, 7 (4)
4. Sumida E., (2004) The effects of oral ingestion of collagen peptide on skin hydration and biochemical data of blood. Journal of Nutritional Food 7 (3): 45-52
5. Matsuda, et al., (2006) Effects of ingestion of collagen peptide on collagen fibrils and glycosaminoglycans in the dermis. J Nutri Sci Vitaminol 52: 211-215
6. Journal of Investigative Dermatology (1995) 105, 285–290; doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12318471 Reduced Type I and Type III Procollagens in Photodamaged Adult Human Skin Harvinder S Talwar, Christopher E M Griffiths, Gary J Fisher, Ted A Hamilton and John J Voorhees. Department of Dermatology, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan, U.S.A.. Received 27 January 1994; Revised 24 March 1995; Accepted 2 May 1995.
7. Tak, Young Jin et al. “Effect of Oral Ingestion of Low-Molecular Collagen Peptides Derived from Skate (Raja Kenojei) Skin on Body Fat in Overweight Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.” Marine drugs vol. 17,3 157. 7 Mar. 2019, doi:10.3390/md17030157

